Since the discovery of tantalum in 1802, the understanding and development of tantalum have had a long history. Tantalum metal is characterized by corrosion resistance, hard quality, high melting point, good thermal conductivity, good affinity with the human body, and easy processing, which is widely used in the fields of metallurgy, chemical industry, atomic energy, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices.

Biocompatibility test of tantalum metal
Biocompatibility refers to the concept of various biological, physical, and chemical reactions resulting from interactions between materials and organisms. Generally speaking, it is the degree of compatibility between the material and the human body after implantation, that is, whether it will cause a toxic effect on human tissue.
The principle of biosafety is to eliminate the destructive effect of biological materials on human organs, such as cytotoxicity and carcinogenicity. If biomaterials are to be successful, they must at least be accepted by the host without harmful effects. Therefore, biological safety evaluation, that is, biological evaluation, should be carried out on biological materials.
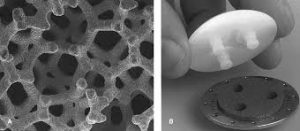
Insoluble tantalum salt is not absorbed by the human body through oral or local injection, and the absorption amount of soluble tantalum salt in the gastrointestinal tract is very small. Once tantalum enters the body, the main carrier responsible for the removal of tantalum is phagocytes. In the body, phagocytes can survive and have no cellular degeneration after 1h exposure to tantalum dust, with only a significant increase in glucose oxidation. Under the same conditions, silica dust can cause severe cytoplasmic degeneration and death of phagocytes, indicating that tantalum is non-cytotoxic.
Through abundant domestic and foreign materials, it is found that porous tantalum has the following advantages compared with titanium alloy.
The advantages of porous tantalum nails are one with the advantages of metal materials. After implantation, as the bone tissue grows, the fixation strength of porous tantalum nail will gradually increase. Meanwhile, as the bone tissue grows, blood circulation is also introduced into the nail body, which is conducive to preventing the occurrence of fracture nonunion and femoral head necrosis. The porous tantalum nail has excellent biocompatibility with bone. It does not need to be taken out after implantation, which can effectively prevent the risk of fracture after the removal of internal fixation. Therefore, porous tantalum nail has a good long-term effect in the treatment of femoral neck fracture and has a broad application prospect in other disciplines of orthopedics and medicine.
Application case of tantalum nail
Porous tantalum nail implantation is an ideal minimally invasive surgical treatment for the treatment of early Avascular Necrosis of Femur Head (ANFH) in adults. It has unique physical and biological advantages and is expected to achieve therapeutic effects that traditional therapies do not, as well as in line with the current concept of minimally invasive. For osteonecrosis in stage Ⅰ and Ⅱ young patients, it can relieve pain and minimize complications, at least slow down or even avoid the joint replacement, but the long-term curative effect is yet to be large sample especially central level and long-term follow-up.
Stanford Advanced Materials supplies high-quality tantalum products to meet our customers’ R&D and production needs. Please visit http://www.samaterials.com for more information.
