Tantalum metal (Ta) has excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point, high strength, and abrasion resistance, which has been widely used in aircraft, rockets, and other heat-resistant materials as well as industrial fields requiring high-strength parts. In addition, tantalum metal has good physical and mechanical properties and good biological compatibility, which makes it a new kind of biological material after titanium metal.

Nowadays, tantalum metal has been widely used in oral implant implantation, femoral head necrosis treatment, coronary artery stent implantation, acetabular prosthesis implantation, surgical suture line production, and other medical fields. The application of medical tantalum and porous tank in stomatology is introduced below.
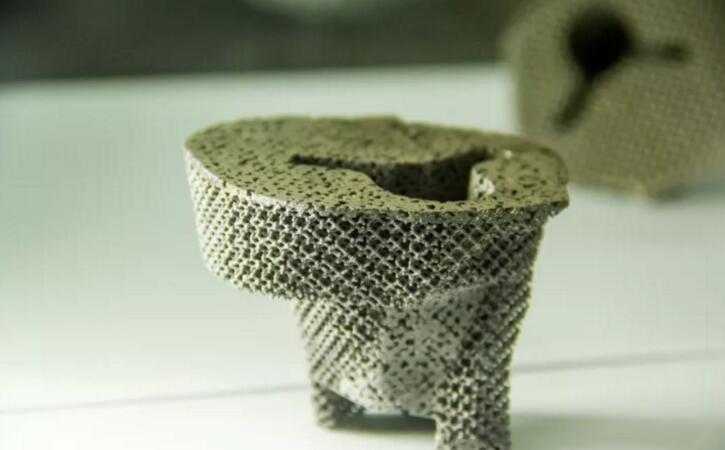
Tantalum has been used as an implant material in the repair and treatment of patients with missing teeth. With the development of science and technology, porous tantalum has also been tried to be used in the field of implants. Due to its outstanding mechanical properties, biological properties, elastic modulus equivalent to bone tissue, and high friction coefficient, it can provide good bone bonding and initial stability for the implant, which is called a bone trabecular implant. In addition, its elastic modulus (between the cancellous bone and dense bone) is the same as that of bone tissue, which enables the implant to disperse the dental forces into the surrounding bone during long-term oral functional load, thus avoiding stress concentration.
Experiments have shown that traditional implants can absorb 30% of the load energy, while porous tantalum implants can absorb 50% to 75%. The high friction coefficient makes tantalum have good initial stability in the process of implant implantation, so as to improve the bonding rate of implant teeth, especially for the implant patients with poor bone quality. The three-dimensional structure of porous tantalum has pores, which are conducive to the attachment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblasts on its surface, and the pore structure is similar to bone tissue, which provides a good scaffold for the growth of bone tissue.

Relevant studies have confirmed that porous tantalum granules have a good ability to induce osteogenesis, and its effect on repairing jaw defects is better than that of bio-oss bone powder commonly used in clinical practice. The porous tantalum granules and bio-oss bone powder were implanted into the defect area of the right and left mandible of beagle dogs respectively. Three months later, gross specimens, X-ray images, and hard tissue sections showed that porous tantalum granule group had a higher bone formation amount and bone tissue maturity than the control group.
Due to their good biocompatibility, tantalum and porous tantalum have important clinical value and application prospects in many fields of medicine, such as stomatology, bone surgery, cardiovascular surgery, and biomedical engineering. The application of surface modification technology will enable tantalum metal and porous tantalum to have more excellent biological properties, thus greatly improving the ability of tantalum and porous tantalum implants to combine with the surrounding bone interface.
Please visit http://www.samaterials.com for more information.
