Introduction
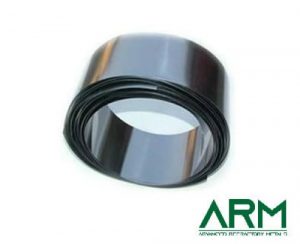
Among its many forms, tantalum foil is particularly noteworthy for its flexibility, biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and radiopacity. These properties make tantalum foil an essential material in the production of medical devices and implants, ensuring both safety and effectiveness in various healthcare settings. This article explores the reasons behind tantalum foil’s growing prominence in the medical field and its specific applications.

Unique Properties of Tantalum Foil
- Tantalum foil is a thin, highly ductile sheet of metal that can be easily manipulated into complex shapes without cracking or losing strength. This makes it ideal for applications where precision and flexibility are crucial, such as in the fabrication of medical implants and devices. Its ductility allows for detailed design and customization, which is often necessary in producing components tailored to individual patient needs.
- One of the most important properties of tantalum is its biocompatibility, meaning it does not induce harmful reactions when in contact with human tissues. This is a critical requirement for materials used in medical devices that will be implanted in the body, as the immune system can sometimes reject foreign substances. Tantalum’s low rate of human exclusion is a significant advantage, particularly when compared to other metals like nickel or chromium, which can trigger allergic reactions in some patients.
- Additionally, tantalum is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in the presence of bodily fluids. This ensures that tantalum implants and devices remain stable and functional over long periods without degradation. The metal’s resistance to both chemical and electrochemical corrosion, even in highly aggressive environments, guarantees that it will not leach harmful substances into the body, providing safety for patients.
Tantalum Foil in Medical Implants
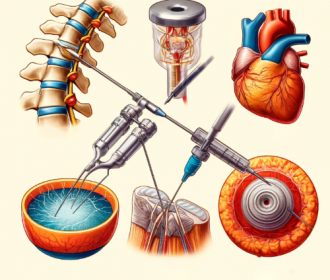
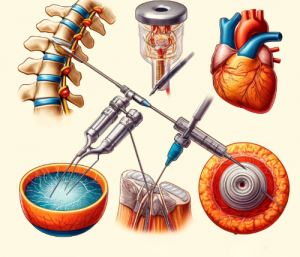
One of the most critical applications of tantalum foil in healthcare is in the production of medical implants. From orthopedic to dental and cardiovascular implants, tantalum foil has become a material of choice for its durability and long-term performance.
- In orthopedic implants, tantalum’s excellent osseointegration—the ability to bond with bone—makes it particularly useful in procedures such as joint replacements and bone reconstruction. Tantalum’s porous structure, when needed, allows bone tissue to grow into the implant, creating a stable and strong bond. This property reduces the risk of implant failure and enhances patient outcomes by promoting faster healing and improved mobility. Tantalum foil is also used in dental implants, providing a stable, corrosion-resistant foundation that is less likely to be rejected by the body compared to other metals.
- In cardiovascular medicine, tantalum foil is often employed in the production of stents and other vascular implants. These devices are crucial for keeping blood vessels open and maintaining proper blood flow in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Due to its flexibility and biocompatibility, tantalum foil allows for the creation of stents that are both durable and easy to insert into the body, reducing complications during surgery and recovery.
Related reading: Choose the Right Tantalum Foil for your Application
Radiopacity: A Key Advantage in Medical Imaging
Tantalum’s radiopacity—its ability to show up clearly on X-rays and other imaging techniques—is another significant advantage in medical applications. This property makes tantalum foil an essential material for creating diagnostic and surgical tools that need to be easily identified in medical imaging.

- Tantalum is commonly used in the form of marker bands for catheters and stents. These markers allow healthcare professionals to track the placement and movement of these devices within the body during surgery or other procedures, ensuring precision and safety. The clear visibility of tantalum on imaging devices ensures that surgeons can accurately position devices like stents or catheters, minimizing the risk of errors.
- Radiopaque tantalum markers also play a key role in guiding surgeons during complex operations. For example, in spinal surgeries, tantalum markers can help guide the placement of screws or rods to ensure proper alignment and positioning, reducing the risk of complications. This precision makes tantalum a vital component in modern surgical techniques.
Biocompatibility and Low Human Exclusion
One of the biggest challenges in medical device design is finding materials that the human body will not reject or react adversely to. Tantalum’s biocompatibility makes it an ideal solution for implants and other devices that need to remain in the body for long periods. Unlike some metals that may cause allergic reactions or immune system responses, tantalum is well-tolerated by most patients, significantly reducing the risk of complications.
Tantalum’s low exclusion rate by the body is particularly important in applications where the material must interact directly with tissues and fluids, such as in bone implants, vascular stents, or dental screws. By minimizing the risk of inflammation or rejection, tantalum improves the long-term success rates of these procedures and enhances patient outcomes.
Advancing Medical Technologies with Tantalum Foil
Tantalum foil’s versatility continues to drive innovation in medical technology. Researchers are exploring new ways to use tantalum in areas such as tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and bioactive coatings. For example, tantalum’s ability to create strong bonds with bone tissue makes it a candidate for developing advanced orthopedic implants that promote faster recovery and improved functionality.
Additionally, tantalum foil is being studied for use in creating bioactive coatings on medical devices, which could further improve their integration with human tissue and enhance healing processes. As the demand for more advanced, biocompatible materials continues to grow, tantalum foil will play a key role in the future of medical device technology.
Conclusion
Tantalum foil has found a prominent place in modern healthcare due to its flexibility, biocompatibility, and resistance to corrosion. Whether in orthopedic implants, dental devices, or cardiovascular stents, tantalum foil offers significant benefits that contribute to improved patient outcomes and the long-term success of medical procedures.
With ongoing advancements in medical technology, tantalum foil’s applications are likely to expand, further cementing its status as a crucial material in the medical field. For more tantalum products, please check Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM).











Recent Comments